Introduction
The Internetworks library in NetSim supports various protocols across all the layers of the TCP/IP network stack. These include Ethernet, Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), Wireless LAN – 802.11 a / b / g / n / ac /ax / p and e (EDCA), Internet Protocol (IP), Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), Virtual LAN (VLAN), User Datagram Protocol (UDP), and routing protocols such as Routing Information Protocol (RIP), Open Shortest Path First (OSPF).
An internetwork is generally a collection of two or more networks (typically LANs and WLANs) which are interconnected to form a larger network. All networks in an Internetwork have a unique network address. Routers interconnect different networks.
Users can use the following devices to design Internetworks: wireless node, wired node, switch, router, and access point (AP). Wired nodes (term for computers, servers etc.) connect via wired link to switches or routers, and wireless nodes connect via wireless links to Access Points (APs). Multiple links terminate at a switch/router, which enables connectivity between them. Many switches/routers are present in an internetwork to connect all the end-nodes. The end-nodes provide and consume useful information via applications like data, voice, video etc.
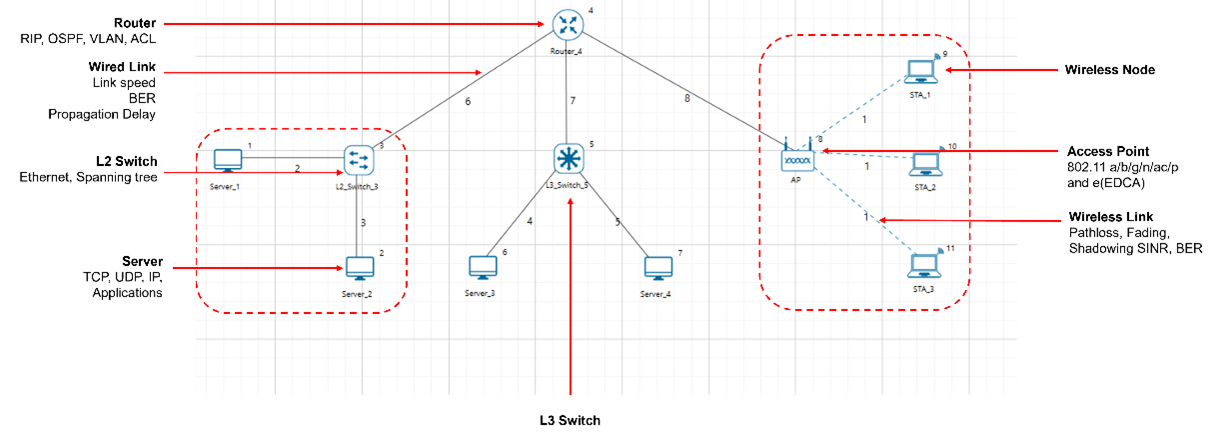
Figure-1: A typical Internetworks scenario in NetSim

Figure-2: The Result dashboard and the Plots window shown in NetSim after completion of a simulation.