Tactical Data Links
Model, simulate and analyze the performance of a tactical data link for a national aerospace company
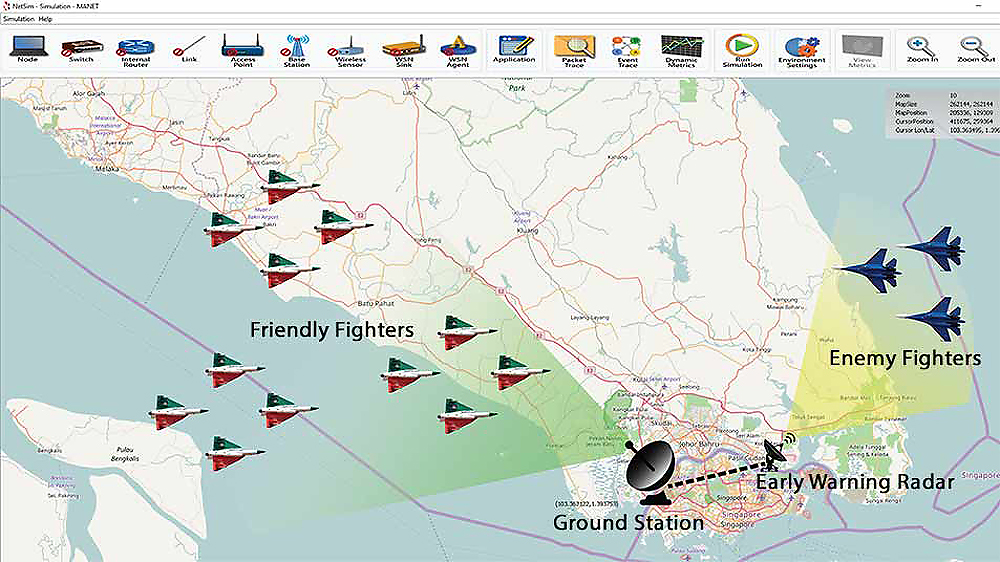
- A Ground Station (GS) is connected to the Early Warning Radar (EWR), via ground network infrastructure
- The GS starts up the network, does the time slot assignment, generates the crypto key and the frequency hopping pattern
- GS then broadcasts the Air Picture to all friendly aircraft
- Friendly aircraft broadcast their positions periodically to one another and to the GS
- When enemy aircraft is detected by the EWR it transmits information to the GS
- GS in turn broadcasts the updated Air Picture to friendly aircraft, which then engage the enemy
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Grid Length | 300x300 km |
| Slot Duration | 50 ms |
| Encryption | AES256 |
| Bits per slot | 2500 bits |
| RF Power | 20 W |
| Modulation | QPSK |
| RX Sensitivity | -108 dbm |
Performance Analysis
A comprehensive set of simulation runs was conducted to evaluate system performance across a wide range of input parameters. Key observations from the analysis of simulation results include:
Signal Quality Issues
- The RF propagation losses resulted in a high Bit Error Rate (BER).
- This high BER led to an unacceptable number of errors in Recognized Air Picture (RAP) packets.
Resource Allocation Inefficiency
- The current round-robin slot allocation method didn't provide immediate time slot availability for the Ground Station (GS).
- This inefficiency potentially impacts real-time communication capabilities.
Conclusions and Recommendations
Optimize Data Transmission
- Reduce the size of Recognized Air Picture (RAP) packets to mitigate the impact of high BER.
- This should decrease the overall error rate in RAP data transmission.
Enhance Resource Allocation
- Transition from the current round-robin method to an optimized slot schedule.
- Prioritize slot allocation for the Ground Station (GS) to improve responsiveness.
Future Enhancements
- Consider implementing Layer 3 routing in future iterations.
- This addition could facilitate more efficient communication between different network segments.